Mobile Technology Explained
This page contains:
How has mobile phone technology developed?
What does the G in mobile technology stand for?
What is 5G?
Can I get 5G?
What is an eSIM?
What are call, text, and data allowances?
How much mobile data am I using?
Non-ionising radiation information
Today’s mobile phone services include phone calls (voice), text messages (SMS), and internet (data), which are delivered through an interconnected network of mobile telephone masts. This technology has greatly evolved over the past three decades.
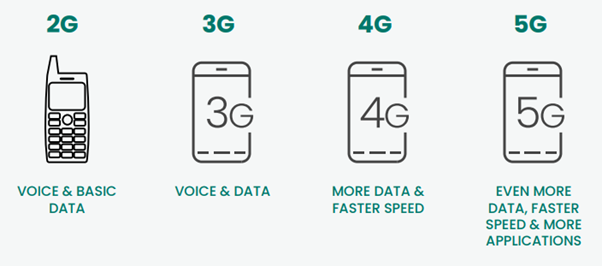
How has mobile phone technology developed?
The first national mobile service in Ireland was 1G, launched back in 1985 Mobile technology has evolved since, seeing 2G first launched in 1993, 3G in the early 2000s, 4G in the early 2010s, and, most recently, with the rollout of 5G in the 2020s.
Each generation brings with it upgraded speeds and capabilities that allow us to do more with our mobile devices.
What does the G in mobile technology stand for?
The ‘G’ stands for the ‘Generation’ of mobile phone technology, for example, 4G is the fourth generation. Each evolution has been capable of faster mobile internet (data) services, which has enabled year-on-year growth in data consumption, the mobile service most used by Irish consumers.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks and the latest development. 5G technology is faster, has fewer delays, and more data can be sent and received at one time compared with previous generations. As a result, 5G-focused developments in connected vehicle technology, immersive gaming, and smart home devices are on the horizon.
5G will operate alongside other technologies enabling faster data speeds and enhanced connectivity between wireless devices.
Can I get 5G?
More and more mobile providers are offering a 5G service and expanding their 5G coverage throughout Ireland. If you want to see how coverage currently looks and where 5G coverage is available, please see our outdoor coverage map.
Please be aware that while 5G is becoming more and more prevalent, not every package provides 5G and some devices may not be compatible. If you want to find a plan that best meets your needs, visit our Compare tool to help you choose.
Our 5G and the evolution of mobile technology page provides more information.
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM is a digital version of a traditional SIM card, built into most modern mobile handsets. Instead of inserting a physical SIM, a ‘blank’ eSIM is already embedded inside your handset.
This eSIM is set-up by downloading certain SIM related data from the mobile provider, a process which is often initiated by scanning a QR code. It means you don’t need to go to a store or wait for a SIM card to arrive in the post. It’s a faster, easier way to connect to a mobile network or switch to a new provider.
Since most modern mobile handsets can take one or more eSIMs, usually in addition to a physical SIM, it means that most mobile handsets are now dual-SIM enabled. This opens up the possibility to have multiple phone numbers, such as a work phone number and a personal phone number on the same device, as two different SIMs will allow you to use different numbers.
An eSIM roaming plan also allows you to travel and stay connected more easily. For more information, see here.
What are call, text, and data allowances?
Many mobile phone plans (be they bill pay or prepay) offer unlimited data, calls, and or texts. Even though these plans may be advertised as unlimited, they might include a cap on how much data you can use, minutes of calls you can make, or the number of texts you can send within a specified period (usually a month).
This means that if you exceed any of these caps you may need to pay additional charges. Information regarding these caps and the price for going over your cap will be included in the terms and conditions of your contract. See the contracts section of the website for more information.
How much mobile data am I using?
Here are some common uses of your mobile phone and examples of estimated data consumption based on these uses. These numbers are very approximate and can vary significantly due to a range of factors:
| Sending 1 email | 20KB – 100KB |
| 1 social media update (with photo) | 350KB – 2MB |
| 1 hour of web browsing | 10MB – 100MB |
| Streaming 1 hour of music | 28MB |
| Downloading 1 app | 40MB – 400MB |
| Streaming 1 hour of basic quality video | 300MB |
| Streaming 1 hour of ultra-high-definition video | 7GB |
*1 kilobyte (KB) is 1,000 bytes, 1 megabyte (MB) is 1,000 kilobytes, 1 gigabyte (GB) is equal to 1,000 megabytes. Precise estimates would depend on a range of factors, and these estimates are for illustrative purposes only.
Using mobile data while in another country may cost you extra – the cost depends on if you are in the EU and how much data you use. We have more information on data usage and your rights when roaming in the EU and ‘Roam like at home’ inclusive countries, or outside the EU.
Non-ionising radiation information
Non-ionising radiation includes radio waves emitted from mobile networks, infrared radiation and visible light. Please visit here for further information.